|
|
|
|
Family: Betulaceae
[Betula bhojpattra var. japonica Shirai, moreBetula bhojpattra var. subcordata Regel, Betula ermanii f. ganjuensis (Nakai) T.Shimizu, Betula ermanii f. nipponica (Maxim.) Koidz., Betula ermanii subsp. lanata (Regel) A.K.Skvortsov, Betula ermanii var. acutifolia H.J.P.Winkl., Betula ermanii var. brevidentata C.K.Schneid., Betula ermanii var. communis Koidz., Betula ermanii var. corticosa Nakai, Betula ermanii var. ganjuensis (Koidz.) Nakai, Betula ermanii var. genuina Regel, Betula ermanii var. incisa Koidz., Betula ermanii var. japonica Koidz., Betula ermanii var. lanata Regel, Betula ermanii var. macrostrobila Liou, Betula ermanii var. nipponica Maxim., Betula ermanii var. parvifolia Koidz., Betula ermanii var. saitoana (Nakai) Hatus., Betula ermanii var. subcordata Koidz., Betula ermanii var. yingkiliensis Liou & Z.Wang, Betula ganjuensis Koidz., Betula incisa (Koidz.) Koidz., Betula lanata (Regel) V.N.Vassil., Betula longilobata Sipl., Betula nikoensis Koidz., Betula paraermanii V.F.Vassil., Betula prochorowii Kuzen. & Litv., Betula saitoana Nakai, Betula shikokiana Nakai, Betula ulmifolia var. glandulosa H.J.P.Winkl., Betula vulcani H.L?., Eleocharis pellucida f. attenuata (Franch. & Sav.) Ohwi] |
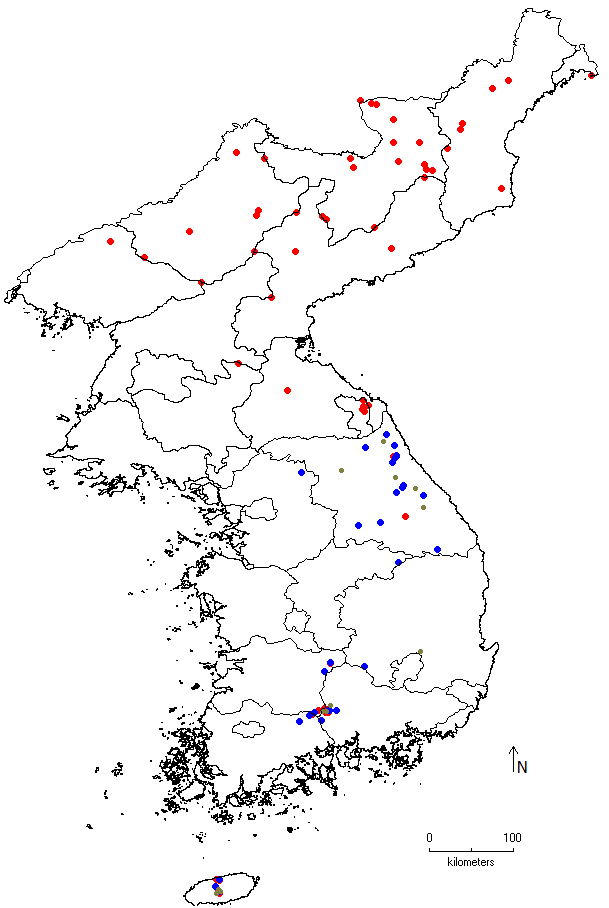
Japan Flora: Tree or large shrub with gray-brown to gray-white bark peeling off into thin pieces, the branchlets resinous when young, soon becoming brownish purple; leaves deltoid-ovate to broadly so, 5-10 cm. long, 4-7 cm. wide, acuminate, irregularly mucronatetoothed, rounded to shallowly cordate, thinly pilose on nerves beneath or glabrous except for axillary tufts of brown hairs, the lateral nerves of 7 to 12 pairs, the petioles 1-3.5 cm. long, usually glabrous; fruiting aments 2-3.5 cm. long, 8-10 mm. in diameter, the midlobe linear-lanceolate, the lateral ones nearly orbicular, ascending, 1/3-1/2 as long as the midlobe; nuts broadly obovate, puberulous above, 2-3 mm. long, the wing narrower than die nut. June-July. Mountains; Hokkaido, Honshu (centr. and n. distr.), Shikoku; extremely variable. Kuriles, Sakhalin, Kamchatka, and Korea. var. japonica (Shirai) Koidz. Leaves deltoid-ovate, the lateral nerves of 14 to 15 pairs, the fruiting scales with a nar-row midlobe and rather spreading lateral lobes. Honshu (centr. distr. and Kanto Distr.). China Flora: Tree, up to 20 m tall; bark grayish white, flaking. Young branches densely covered with long villous hairs and resin glands. Bud scales densely covered with silky hairs. Leaves ovate, broadly ovate or triangular ovate, 2-7 cm long, pointed or short-tailed, sparsely covered with long villous hairs above, covered with long villous hairs and resin glands below, with irregularly cuspidate double serrations, 8-12 pairs of lateral veins; petiole 1-2.4 cm long. Female inflorescence ovoid or oblong-globose, 1.5-2.7 cm long, peduncle (1) 3-6 mm long; bracts glabrous, middle lobe oblanceolate, lateral lobes slightly shorter than middle lobe. Nutlets obovate or obovate-elliptic, 2.5-3 cm long, membranous wings 1/3-1/2 as wide as the fruit. It is native to Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia and Hebei. It grows in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests at an altitude of 1,000-1,700 meters or in pure forests in wetlands near streams. It is also distributed in Japan, northern Korea and Kamchatka, Russia. The material is relatively hard and is used for construction, utensils, matchsticks, sleepers, etc. The leaves can be used as dyes [translated from Higher Plants of China] Korea Flora: Alpine deciduous tree or shrub. Height 7-8m. Bark grayish-red-brown to almost whitish-gray, peeling in paper-like layers that remain attached to trunk. Winter Buds and Stems: Buds elongate-globose with sharp apex, 4 bud scales; terminal and lateral buds similar (7-12mm). Young branches initially pubescent becoming glabrous, developing dots and punctate lenticels. Leaf scars crescent-shaped. Leaves: Alternate, triangular-ovate, apex acuminate, base nearly rounded. Size 5-7(10)cm × 3.5-5(6)cm, irregularly serrate; 7-11(14) pairs of lateral veins; upper surface glabrous; lower surface with dots and pubescent along veins. Petiole 5-30mm long. Flowers: Female catkins ovoid or oblong, 3cm long; peduncle 3-4mm or almost absent. Fruit and Seeds: Nuts erect, 2-3cm long, oblong; central lobe of involucral bracts longer than lateral lobes, linear-oblong; lateral lobes obovate-elliptic. Wings half as wide as nutlet.
Ecological Characteristics: A light-demanding species that grows near the alpine tree line but can form tall trees at lower elevations. Typically grows above 1,000m elevation in Gangwon-do. Forms colonies after forest fires. As a light-demanding species, shows very rapid initial growth in high-light conditions. A pioneer species that initiates growth on slopes and dry areas. Grows at higher elevations than coniferous forests dominated by spruce and fir (above 1,000m in Gangwon-do), becoming a dominant species extending to Far Eastern Russia and northern Hokkaido. In alpine zones, typically grows as a shrub (though tree-form on Mt. Odae), with stems and branches from lateral buds often curved due to snow damage. Shows strong resistance to snow damage, enabling growth at higher elevations than conifers. In Russia, specimens over 500 years old have been found with DBH of 130-180cm and heights of 15-25m. Although light-demanding, grows well under other species' canopies when young. Growing in moist areas and snowmelt zones during summer, this species is relatively resistant to forest fire damage. Natural regeneration occurs in forest gaps through seed germination. Seed germination is somewhat limited by tall herbaceous layer development. Natural thinning occurs at 15-25 years, and by 60-70 years, it forms pure stand canopies. Often forms pure stands easily along with Quercus mongolica. While forest fires tend to create uneven-aged rather than even-aged stands, this species shows stronger resistance to fire and snow damage compared to spruce or larch, enabling easy formation of pure stands. Sometimes forms mixed forests rather than pure stands due to competition from shade-tolerant species like spruce and fir. |
National University and Korea National Arboretum of Korea Forest Service.